Description
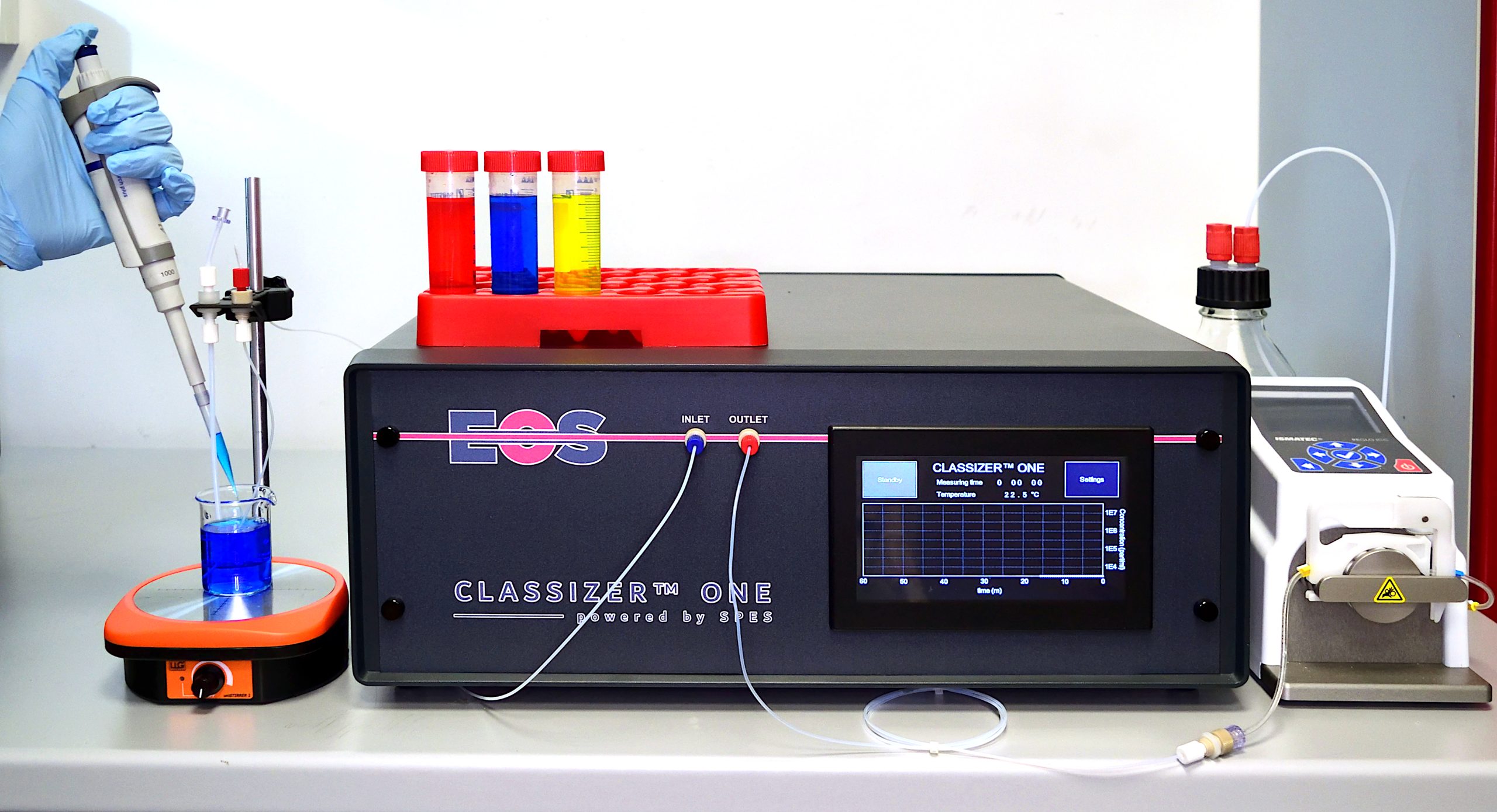
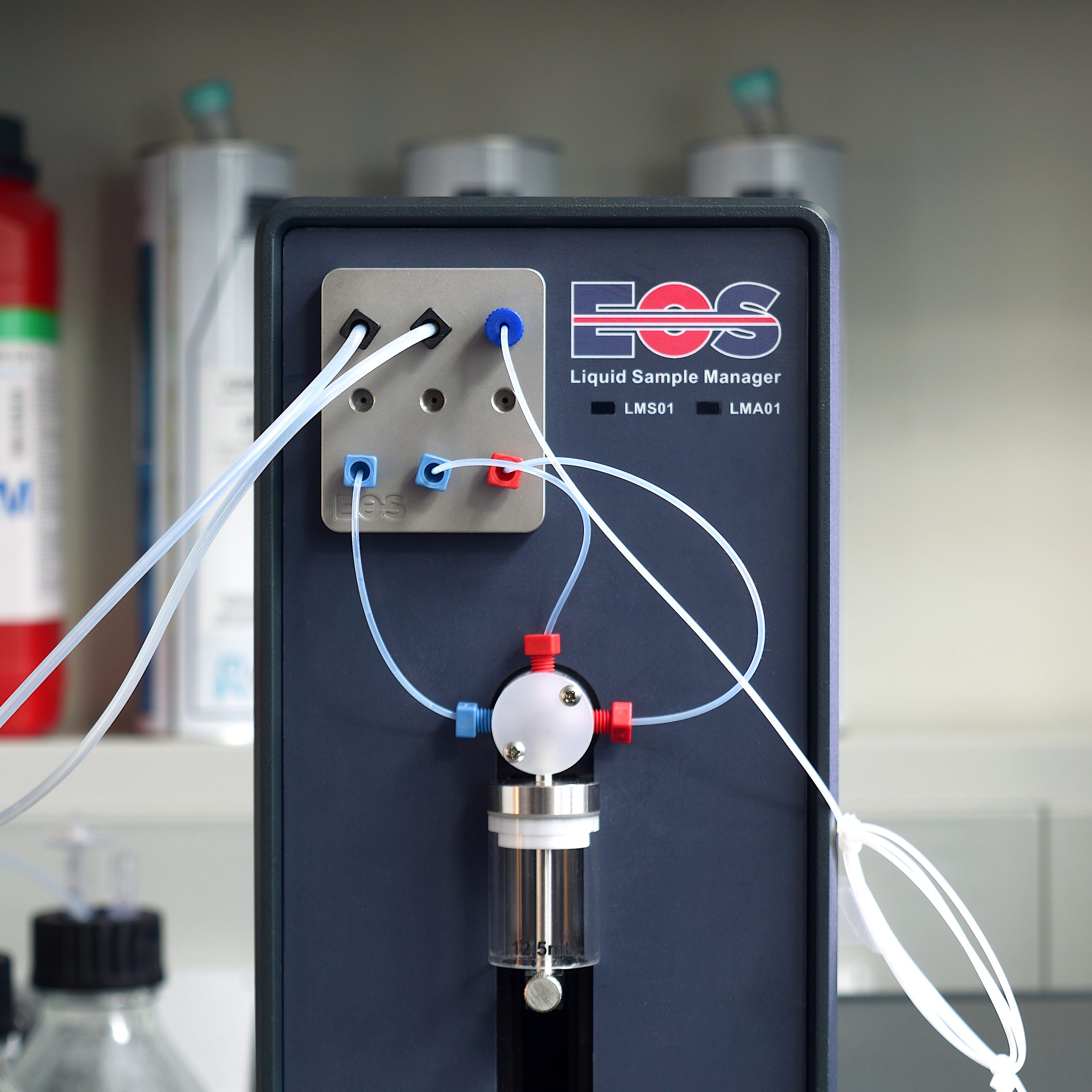
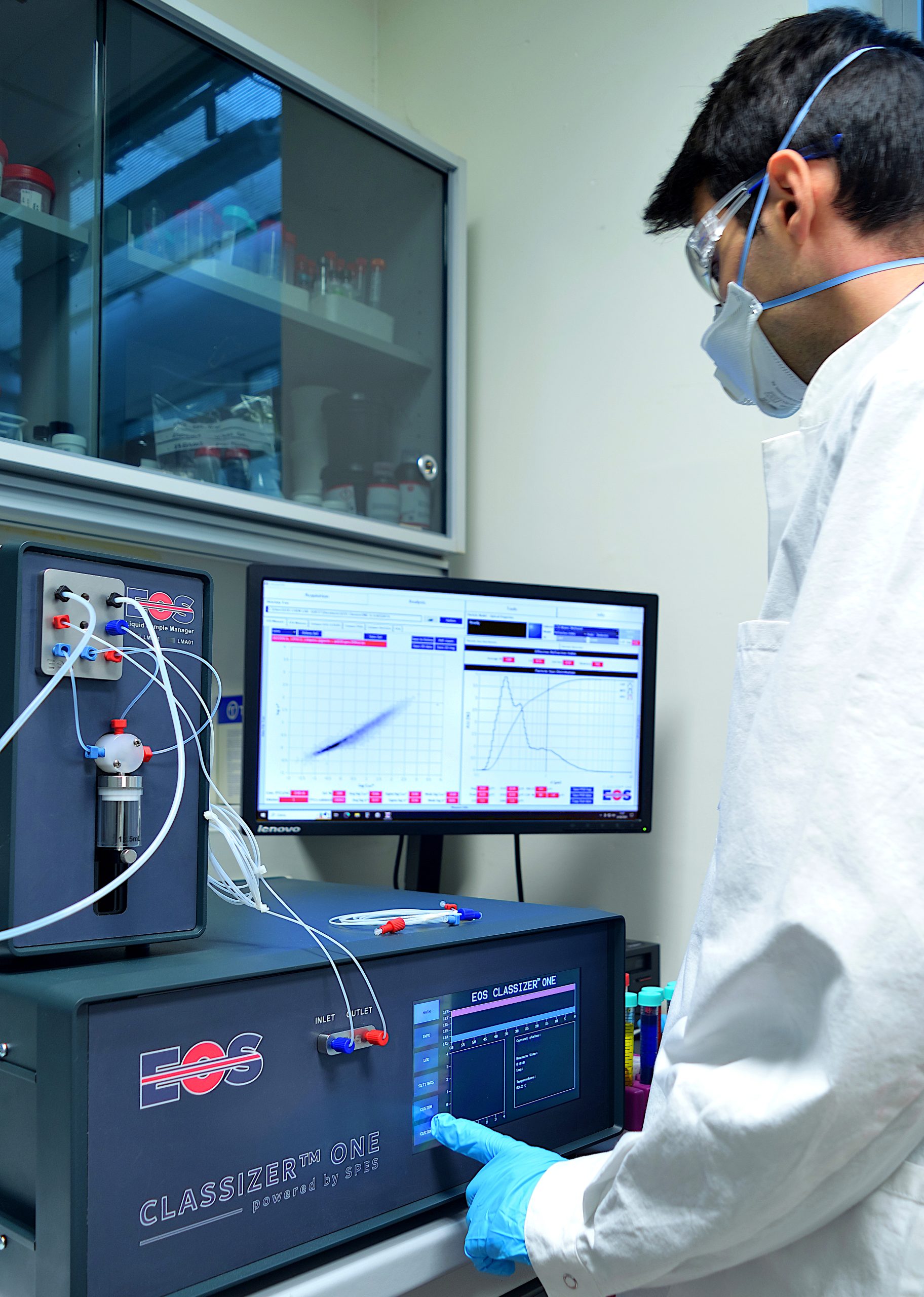
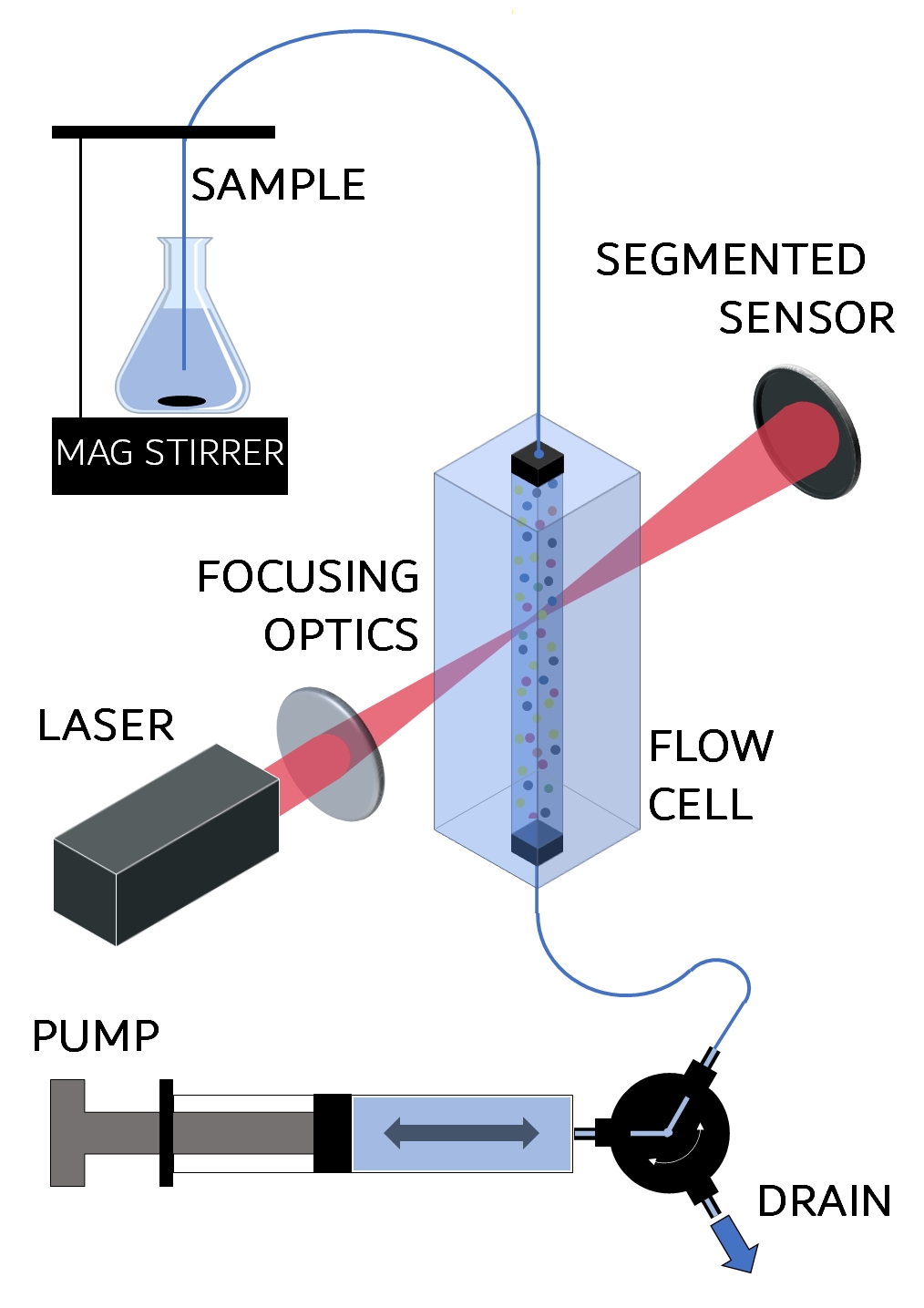
The Single Particle Extinction and Scattering (SPES) method utilises a syringe pump to create a laminar fluid flow of the sample through a laser beam. The laser beam is tightly focussed so that the particles in the sample flow through the narrow waist of the beam between the laser source and a sensor.
IMAGE RIGHT: System overview showing how the sample is fed through the flow cell and sampled by the focussed laser beam. Automated flow using the system pump sends a defined amount of the stirred sample. Single particles pass through the laser beam and produce changing intensity modulations/interference patterns at the sensor plane.
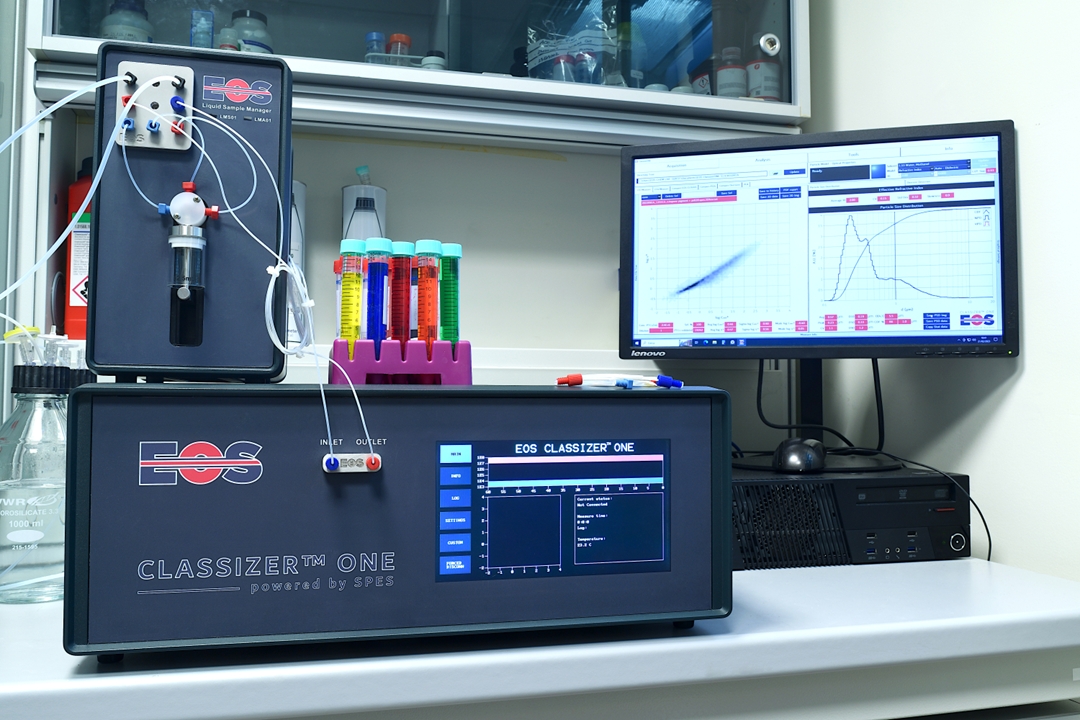
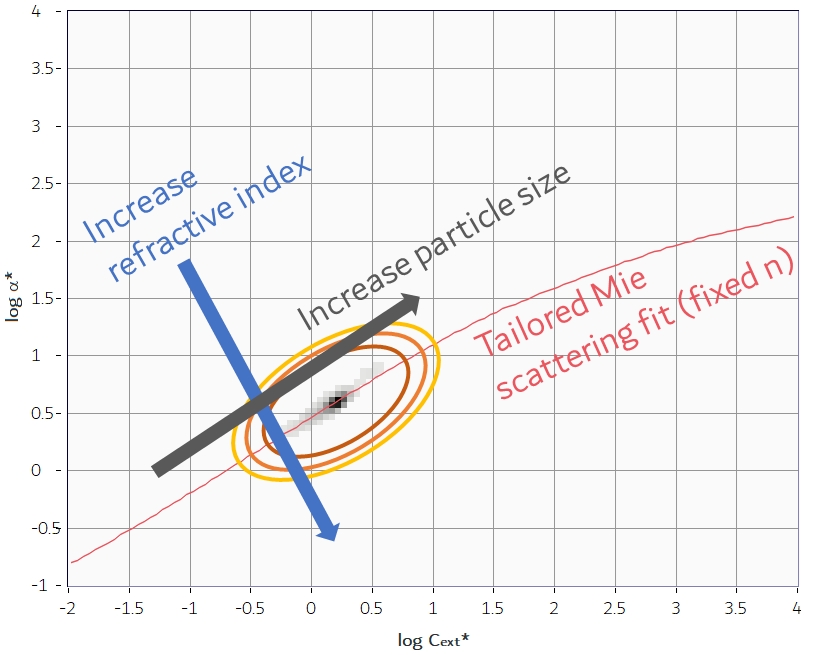
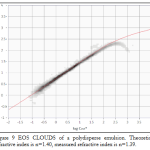
The interference between the un-scattered laser light and the fraction scattered by each particle, at different positions in the beam, allows accurate characterisation of the sample. Light is scattered in different ways by the particles, according to their size, refractive index and structure. The EOS Classizer™ ONE is able to use this information to create 2-dimensional histogram clouds, separating the particles according to their optical properties. Heterogeneous samples produce simultaneously different “clouds” for each particle population which can be individually selected, analysed and compared.
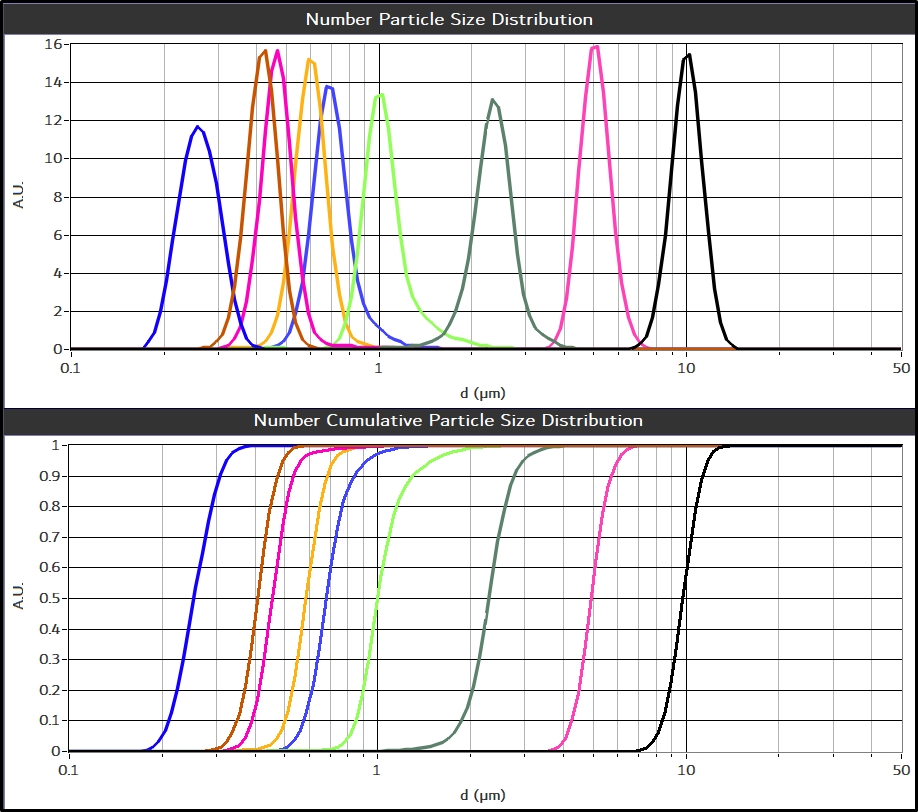
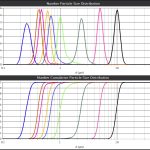
Particle size distribution, numerical concentration and other statistical insights are retrieved from this information and are displayed by individual sample component in heterogenous mixes, for the whole sample, or for each time frame in a Continuous Flow Analysis mode. This includes fully overlapping particle size distributions for each component material.
IMAGE RIGHT: Particle size distribution and number concentration are calculated for different materials in a heterogeneous solution, even for overlapping particle size distributions (PSDs).
Interested in the Classizer™ One? Request a quote or call us on +44(0)1954 232 776 to discuss your requirements.