Nanoparticle Albumin Bound Drug Delivery Technology
The Advantages of Nanoparticle Albumin Bound (nab) Paclitaxel
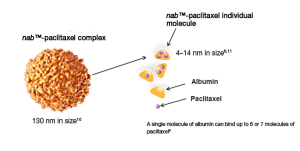
Nanoparticle albumin bound (nab) paclitaxel is a chemotherapeutic delivery platform, used in the treatment of some cancers. It offers several benefits over traditional treatments including enhanced efficiency and improved patient tolerability. Paclitaxel, a taxane antimicrotubule agent, is highly effective in inhibiting cell division but also carries high toxicity; however, when bound to albumin, a biocompatible and biodegradable protein derived from plasma, the toxicity and immunogenicity are significantly reduced compared to traditional solvents like Cremophor EL and ethanol. This makes albumin a favourable carrier for delivering therapeutic agents like paclitaxel to targeted tumor sites, effectively blocking cancer growth, inhibiting cell division, and eliminating cancer cells.
“Paclitaxel is one of the most effective chemotherapeutic drugs ever developed and is active against a broad range of cancers, such as lung, ovarian, and breast cancers. Due to its low water solubility, paclitaxel is formulated in a mixture of Cremophor EL and dehydrated ethanol (50:50, v/v) a combination known as Taxol. To date, paclitaxel albumin-bound nanoparticles (Abraxane®) have been approved by the FDA for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).” – Ping Ma and Russel J. Mumper, Paclitaxel Nano-Delivery Systems: A Comprehensive Review, NIH ( National Library of Medicine) – National Centre for Biotechnology Information. Read the full article>
The Challenges of Albumin Bound (nab) Paclitaxel
Administering albumin-bound paclitaxel drugs through intravenous injection directly into the bloodstream ensures an immediate response. However, it poses challenges in terms of sterilisation during the development and manufacturing process. Additionally, combining two immiscible substances, albumin (aqueous protein) and paclitaxel (solvent-based agent), presents another major challenge: achieving consistent distribution and maintaining a tight particle size distribution, with small particles around 130 nm.
Producing Nab-nanoparticles through Emulsification
The most effective method for creating nab-nanoparticles is emulsification. In this process, paclitaxel, the active ingredient, is dissolved in an organic solvent to form an oil phase. This oil phase is then mixed with an aqueous phase containing an albumin solution. Through high shear processing, a nanoemulsion is created. Finally, the nanoemulsion undergoes solvent removal, sterilisation, and lyophilization (freeze-drying) steps to produce the powdered end product.
The Crucial Role of Microfluidizer® Processing Technology
Microfluidizer® technology plays a crucial role in nanoemulsion applications, including producing nab paclitaxel nanoparticles with precise particle size control. Microfluidizer® processors ensure the creation of stable emulsions with narrow particle size distribution, allowing them to pass through sterilising filters without loss of product or equipment clogging, thus maintaining efficient production. Microfluidizer® technology delivers uniform high shear forces, enabling repeatable results regardless of volume size. Tight particle size distribution is vital in achieving consistent chemotherapeutic production, and Microfluidizer® technology allows for scalability from lab to pilot-scale to manufacturing. By generating narrow particle size distributions, this technology enhances stability and extends the shelf life of the final product.
For more information and learn more about the Microfluidizer® technology for creating nanoemulsions, please visit our Nanoemulsions Solutions Page or contact info@analytik.co.uk and one of our Product Specialists will assist you.